#
📝 Working with methods
A net check method is a set of rules which define a network validation contract (what to call, what to expect). Currently, there are two types of methods: HTTP-code methods and HTTP-content methods. You can use the built-in methods, create your own custom methods, or even create methods at runtime.
#
HTTP-code methods
HTTP-code methods validate the network response based on the HTTP status code returned by the endpoint. For example, the Google 204 method expects a 204 No Content status code.
If the response code matches the expected code, the network is considered reachable.
#
HTTP-content methods
HTTP-content methods validate the network response based on the content returned by the endpoint. For example, the Apple success method expects the response body to contain the text Success.
If the response content matches the expected content, the network is considered reachable.
#
🔧 Creating methods
You can either create methods through the EazyNetChecker editor (which can later be accessed and used in code), or at runtime through code. Methods created during runtime will only exist for the duration of the application session, and won't be saved to the method database.
#
Creating methods in the editor
To create custom methods in the editor, open the EazyNetChecker window by navigating to Window > Hellmade Games > Eazy NetChecker.
From there, go to the Methods tab and click the + button in the Custom methods section. Choose the type of method you want to create (HTTP-code or HTTP-content), fill in the required fields, and click Add.
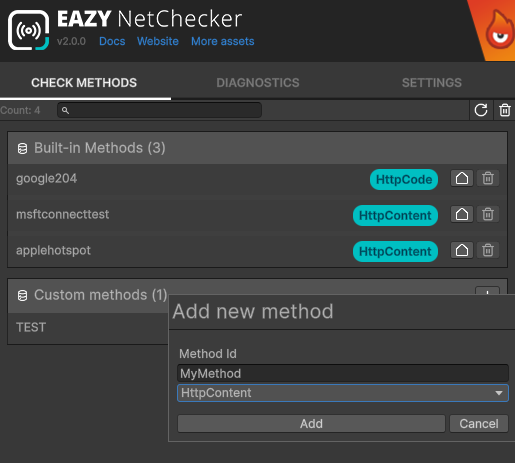
Methods need to have a unique id. You can however give it any display name you want.
#
Creating methods at runtime
You can create methods at runtime by instantiating the appropriate method class and registering it with the method registry. For example, to create and register a custom HTTP-content method at runtime:
var myMethod = new HttpContentNetCheckMethod(
id: "MyNewMethod",
name: "My new method",
url: "https://mydomain.com/ping",
expectedContent: "OK");
EazyNetChecker.MethodRegistry.RegisterMethod(myMethod);Using instances or DI?
If you are using dependency injection, or already has a reference to the method registry instance (INetCheckMethodRegistry), just call RegisterMethod on that instance instead of the static facade.
#
🔎 Accessing & using methods
Built-in and custom methods can be accessed in the exact same way, so any explanation on how to access them apply to both of them
#
Use the default method
If you do not need a specific method, you can use the method you have set as default. If no method is set as default, then the platform default will be used.
You can easily do that through the EazyNetChecker facade, or through EazyNetCheckerConfig if you already have a reference to it
// Using the static facade
var method = EazyNetChecker.GetDefaultMethod();
// Using the config instance
var method = config.GetDefaultMethod();
#
Get a method by id
If you need a specific method, you can get it by its id. For example, to get the Google 204 method:
var method = EazyNetChecker.GetMethod("google204");Or, if you are using DI or have a reference to the method registry instance (INetCheckMethodRegistry):
var method = methodRegistry.GetMethod("google204");
#
Reference method from the inspector
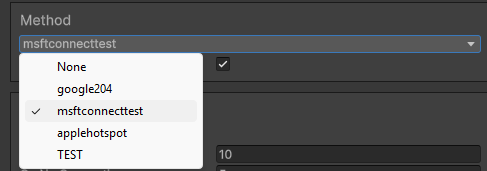
You can also use a method reference (NetCheckMethodReference) to reference a method from the inspector in any of your scripts.
A method picker will appear in the inspector, allowing you to select any built-in or custom method available.
public class MyMonoScript : MonoBehaviour
{
[SerializedField] private NetCheckMethodReference methodReference;
private void Start()
{
var method = methodReference.Resolve();
// Use the method...
}
}
